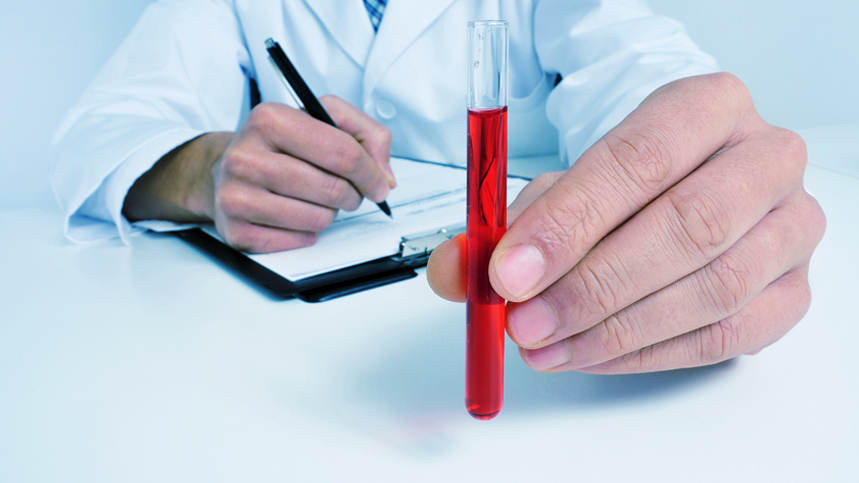
Blood cultures play a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of various infections. They help in identifying the microbial etiology of infections and guide in the selection of appropriate antibiotics. Blood cultures have proven to be an essential tool in antibiotic stewardship and reduction of antibiotic resistance. In this post, we will discuss the role of blood cultures in antibiotic selection and why it matters.
Blood cultures are a diagnostic tool that helps in identifying the causative organism of an infection. The presence of bacteria, fungi, or viruses in the bloodstream can cause sepsis, a severe life-threatening condition. Blood cultures enable the healthcare provider to isolate and identify the infectious agent in the blood. This, in turn, helps in the selection of appropriate antimicrobial agents that will effectively treat the infection.
The results of blood cultures are crucial in the selection of antibiotics. Once the causative organism is identified, antimicrobial susceptibility testing can be performed to determine which antibiotics will be effective. This allows for targeted therapy that can reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance. With targeted therapy, the patient receives the right antibiotic, at the right dose, and for the right duration, which improves clinical outcomes and reduces the risk of complications.
Blood cultures are also essential in the management of fever in patients. Patients with fever of unknown origin (FUO) or prolonged fever require blood cultures to be taken to identify the causative organism. This helps in the selection of the right antimicrobial therapy that will effectively treat the infection. This is especially important in immunocompromised patients who are more susceptible to infections.
Blood cultures also guide in the discontinuation of antibiotics. Once the results of blood cultures come back, the healthcare provider can discontinue broad-spectrum antibiotics and transition to more targeted therapy. This reduces the chance of antibiotic resistance, side effects, and reduces healthcare costs. Monitoring the effectiveness of antibiotics through the use of blood cultures can help determine when it is appropriate to stop treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blood cultures play a crucial role in antibiotic selection. They help in identifying the causative organism of infections, guide in the selection of appropriate antibiotics, and reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance. Blood cultures are essential in the management of fever, fever of unknown origin and immunocompromised patients. Healthcare providers need to understand the importance of blood cultures in antibiotic stewardship and improving clinical outcomes. By utilizing blood cultures appropriately, we can reduce the risk of antimicrobial resistance and improve patient outcomes.
WANT TO BOOK HEALTH CHECKUP ?
Recent Blogs
Understanding Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Staging
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a type of liver cancer that usually affects individuals...
30-11-2023
Protecting Your Skin: Vital Tips for Sun Safety and Self-Examinations
Summer is here, and we all are ready to soak up some sunshine after long and dreary winter...
30-11-2023
Preventing Liver Cancer: The Role of Hepatitis Vaccination
Liver cancer is a deadly disease that affects millions of people worldwide. While there...
30-11-2023