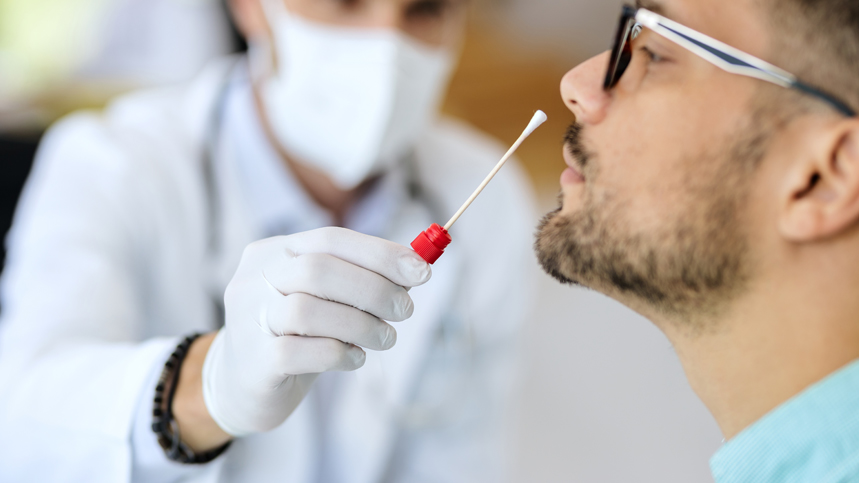
The outbreak of COVID-19 has brought the spotlight onto testing methods like never before. With PCR testing emerging as the most reliable and accurate method, it has become a vital tool for microbiologists and virologists. PCR, or Polymerase Chain Reaction, is a process that enables scientists to rapidly amplify segments of DNA. This process is an essential tool in molecular biology and microbiology, where a small amount of target DNA needs to be amplified for diagnosis or research purposes.
PCR Testing: How Does It Work?
PCR testing is based on a pretty simple process that utilizes the power of enzymes. Using a sample of DNA, PCR testing amplifies sequences of DNA by replicating them several times over. The process involves three fundamental stages- Denaturation, Annealing, and Extension. The sample DNA is first heated to separate the two strands of DNA. This first stage is denaturation. The DNA is then cooled, allowing primers to bind to the denatured, single-stranded DNA, and enter the extension phase. Finally, Taq Polymerase, an enzyme that can add nucleotides to the growing primer strand, is added, and the DNA fragments are replicated. During each cycle of the process, the number of target DNA segments doubles- making PCR testing an incredibly effective way of producing highly accurate results.
Benefits of PCR Testing
PCR testing is one of the most advanced and accurate methods of identifying and analyzing DNA segments. Some of the benefits of this technology include rapid results, high accuracy, and sensitivity. PCR testing is so precise that it can detect even the slightest traces of DNA from a sample. This technology has advanced to the point that it can even be used to identify mutations in DNA, making it an indispensable tool for diagnosing diseases like cancer. PCR testing is also cost-effective and highly scalable. With the ability to find a tiny fragment of DNA, PCR testing has become one of the most popular diagnostic methods used in medical labs across the world.
Applications of PCR Testing in Microbiology and Virology
PCR testing has numerous applications in the fields of Microbiology and Virology. Some of the most common uses for PCR testing in microbiology include identifying bacterial infections, detecting antibiotic-resistant genes, and identifying pathogens. Recently, PCR testing has also been applied to the study of viruses- particularly the COVID-19 virus. PCR testing is used in COVID-19 testing to detect the presence of the virus in a patient's nasal swabs or saliva samples. By identifying the specific DNA fragments of the virus, PCR testing can determine if a person is infected with COVID-19 or not.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PCR testing has become a core method utilized in microbiology and virology for its advanced ability to amplify segments of DNA. It is a highly sensitive, accurate, and effective method to diagnose diseases and identify DNA sequences. PCR testing has played a pivotal role in detecting diseases, identifying their cause, and monitoring the spread of illnesses. Currently, PCR testing has provided a much essential tool in battling the COVID-19 pandemic globally. With continued advancements in PCR testing technology, it is safe to say that its applications in Microbiology and Virology are limitless.