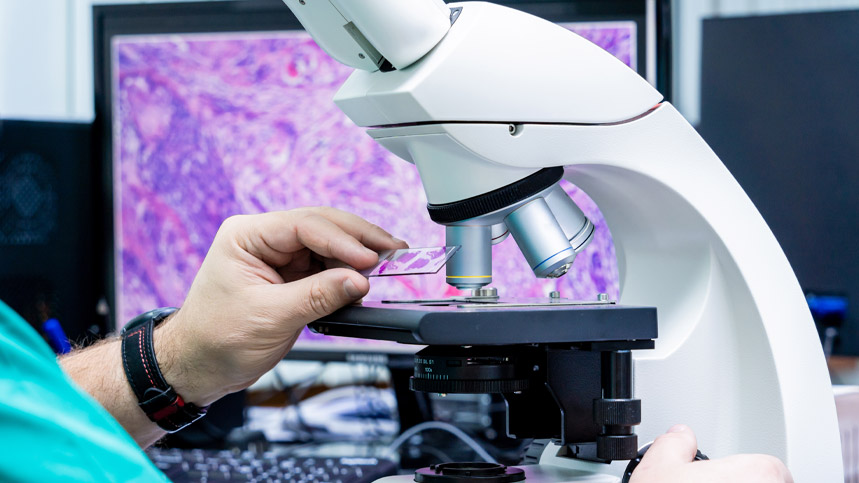
Histopathology is a process of microscopic examination of tissues and cells to identify any abnormalities or diseases. It is an essential component in the diagnosis of cancer and helps in deciding the type of treatment a patient requires. Histopathology allows doctors to examine the cancer tissue's microscopic details to determine the type of cancer, the stage of cancer, and how aggressive the cancer cells are.
Identifying the Type of Cancer
Histopathology is the first step in diagnosing cancer and helps in determining the cancer's type, such as breast cancer or lung cancer. Pathologists examine the cancer cells' characteristics, including their size, shape, and organization, to identify the cancer's type. Knowing the cancer type helps the doctor to decide the best course of treatment for the patient.
Determining Cancer Stage
After identifying the type of cancer, histopathology helps in determining the stage of cancer. The stage of cancer is its extent within the body and how far it has spread. Based on the stage, doctors can recommend a suitable treatment option, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these therapies.
Assessing Cancer Cell Activity
The histopathology test can assess the cancer cells' activity and how aggressive they are. It helps in identifying the grade of cancer, ranging from low to high, based on the cell's irregularity in their shape and growth rate. High-grade cancer requires more aggressive treatment to fight the cancer cells effectively.
Monitoring Treatment Response
Once the treatment begins, histopathology is essential in monitoring the treatment's effectiveness and how the cancer cells respond to it. The pathologist examines the cancer cells to determine if they are responding to the treatment, and if not, the doctor can adjust the treatment plan accordingly. It is crucial to repeat the histopathology test periodically to monitor the progress of the cancer.
Identifying Recurrence of Cancer
Histopathology is also crucial in detecting cancer's recurrence after treatment. It helps in identifying any abnormalities in the cancer cells and determining whether the cancer has relapsed. If the pathologist detects cancer recurrence, the doctor can recommend further treatment or change the current treatment plan.
Conclusion
Histopathology is an essential diagnostic tool in cancer treatment that helps doctors determine the type, stage, aggressiveness, and response to the treatment plan. With the help of histopathology, doctors can provide personalized and effective treatment according to the patient's individual needs. Identifying the cancer cells' characteristics and monitoring the treatment's progress through histopathology helps in making informed decisions about the best course of treatment for the patient. Finally, histopathology plays a vital role in detecting cancer recurrence, helping doctors make timely decisions about further treatment.