
Don't Let Fever Bring You Down
Get Yourself Tested With AMPATH
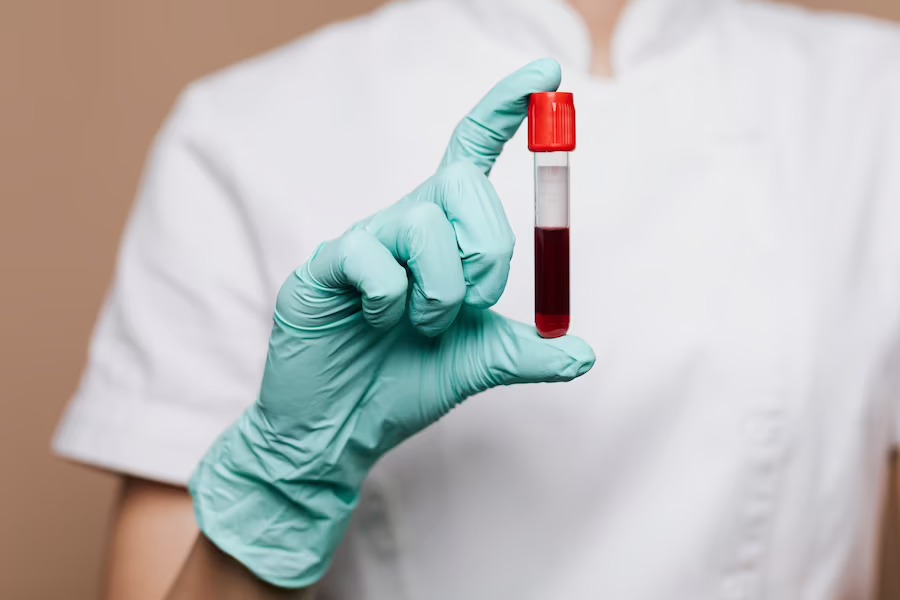
Widal test is a blood test used for diagnosing infections caused by the bacteria Salmonella Typhi. This test can detect the presence of antibodies (agglutinin) in the blood of an infected person, which identifies the causative agent of typhoid fever. The Widal test detects antibodies in the blood that are produced in response to specific antigens found on the surface of the bacteria Salmonella Typhi. This test is simple to perform, and the results can be interpreted quickly and easily.
Principle
The Widal test is based on the principle of detecting antibodies produced by the immune system in response to infection by Salmonella Typhi. The test involves mixing the patient's blood serum (the liquid portion of blood containing antibodies) with a solution that contains inactivated Salmonella antigens. These antigens are specific proteins found on the surface of the bacteria. When the patient's serum is added, the agglutination of bacteria occurs if the patient's serum contains specific antibodies against Salmonella Typhi antigens. The reaction can be observed either by agglutination (clumping) of the bacteria or by measuring the level of antibodies in the blood. A positive Widal test result is determined by the presence of a significant rise in antibody levels compared to a baseline or by the presence of a certain level of antibodies. The interpretation of the results depends on the specific cutoff values established by the laboratory conducting the test.
Procedure
The Widal test involves taking a blood sample from the patient that will be used to detect any antibodies present in the blood serum. The following steps are followed in performing a Widal test:
Step 1: Serum Preparation: The blood sample is collected in a sterile container and allowed to clot. After clotting, the serum is separated from the blood by centrifugation and stored at 4°C until testing.
Step 2: Antigen Preparation: Antigens from Salmonella Typhi are prepared and mixed with a saline solution.
Step 3: Agglutination: Different dilutions of the patient's serum are mixed with the antigen solution and observed for agglutination reaction. Agglutination occurs when the patient's serum contains specific antibodies against Salmonella typhi antigens.
Step 4: Interpretation: The test results are interpreted based on the agglutination reaction observed in different dilutions of the patient's serum. The test results are reported as the highest dilution of serum that shows agglutination.
Uses
Widal test is used for diagnosis and detection of typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever caused by Salmonella typhi or Salmonella paratyphi. The test is used to confirm the presence of salmonella infection in patients with fever, body aches, and other symptoms. The test may also be used to monitor the treatment progress of the disease by comparing the titers of the patient's serum before and after treatment.
Best screening tool
Widal test is a simple blood test to detect Salmonella infections, especially typhoid fever. However, its interpretation requires expertise and knowledge due to occasional false positive or false negative results owing to cross reactivity and lack of adequate antibodies respectively. It is important to understand the principle and the procedure of this test to appreciate its significance fully. If you suspect that you have typhoid fever or any Salmonella infection, consult a healthcare professional. Only they can interpret your test results correctly and provide the appropriate treatment.
If you have the symptoms of typhoid fever such has sustained fever, weakness, fatigue and loss of appetite, do book a widal test today at AMPATH.
Limitations
The Widal test is used as a screening method, and its results must be correlated with clinical symptoms. The test can give false-positive results due to cross-reactivity with other bacterial infections, immunological disorders and it is essential to perform a confirmatory test to rule out the presence of these false-positive results. Also, the test can give false-negative results in the early stages of the infections as antibody production can take some time, and the test may not detect antibodies from the blood serum.
Understanding Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Staging
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a type of liver cancer that usually affects individuals...
30-11-2023
Protecting Your Skin: Vital Tips for Sun Safety and Self-Examinations
Summer is here, and we all are ready to soak up some sunshine after long and dreary winter...
30-11-2023
Preventing Liver Cancer: The Role of Hepatitis Vaccination
Liver cancer is a deadly disease that affects millions of people worldwide. While there...
30-11-2023
Subscription Subscribe to our newsletter and receive a selection of cool articles every weeks
Recent Blogs
Understanding Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Staging
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a type of liver cancer that usually affects individuals...
30-11-2023
Protecting Your Skin: Vital Tips for Sun Safety and Self-Examinations
Summer is here, and we all are ready to soak up some sunshine after long and dreary winter...
30-11-2023
Preventing Liver Cancer: The Role of Hepatitis Vaccination
Liver cancer is a deadly disease that affects millions of people worldwide. While there...
30-11-2023
Enter your details
Set Location
Share Your Feedback
Select Your Location
Top Cities




 Get 15% OFF on 1st order above ₹100 Use code:
Get 15% OFF on 1st order above ₹100 Use code: 